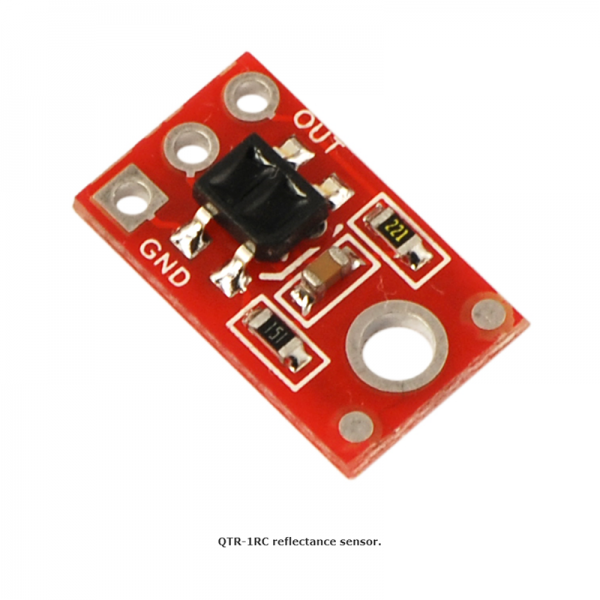
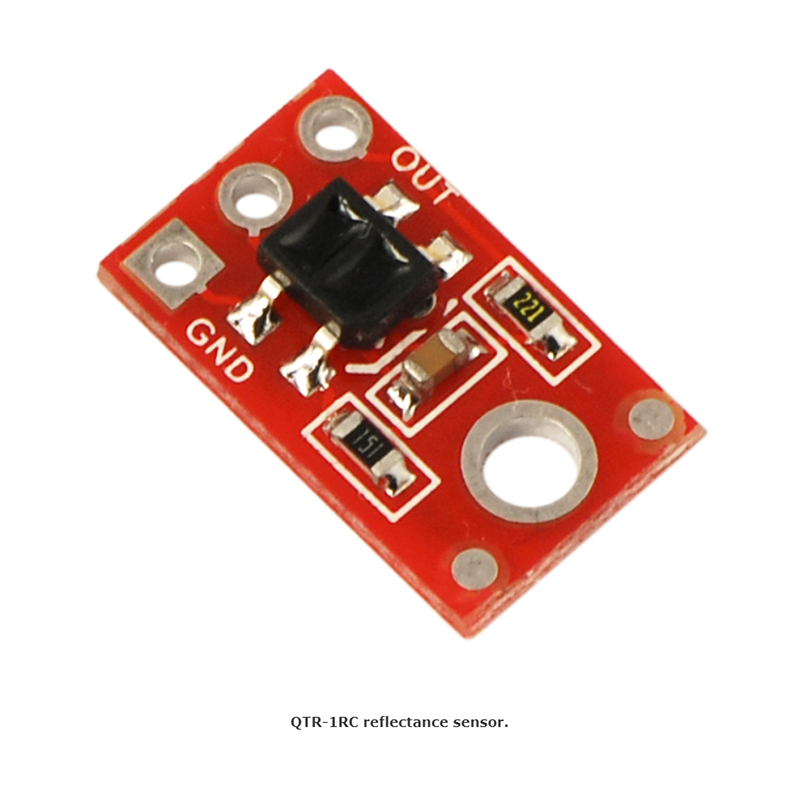
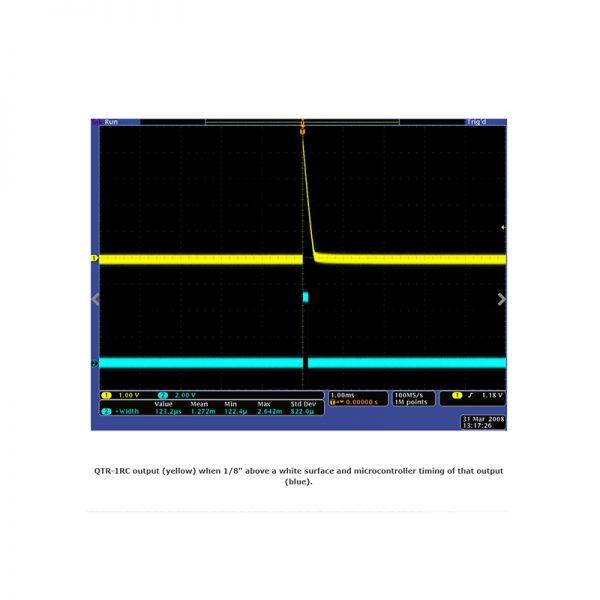
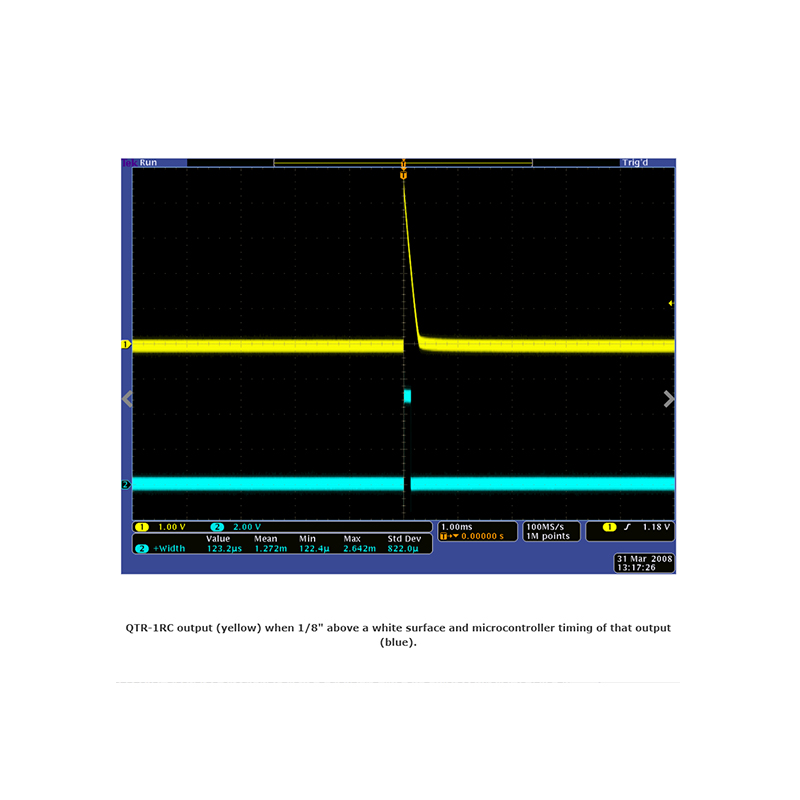
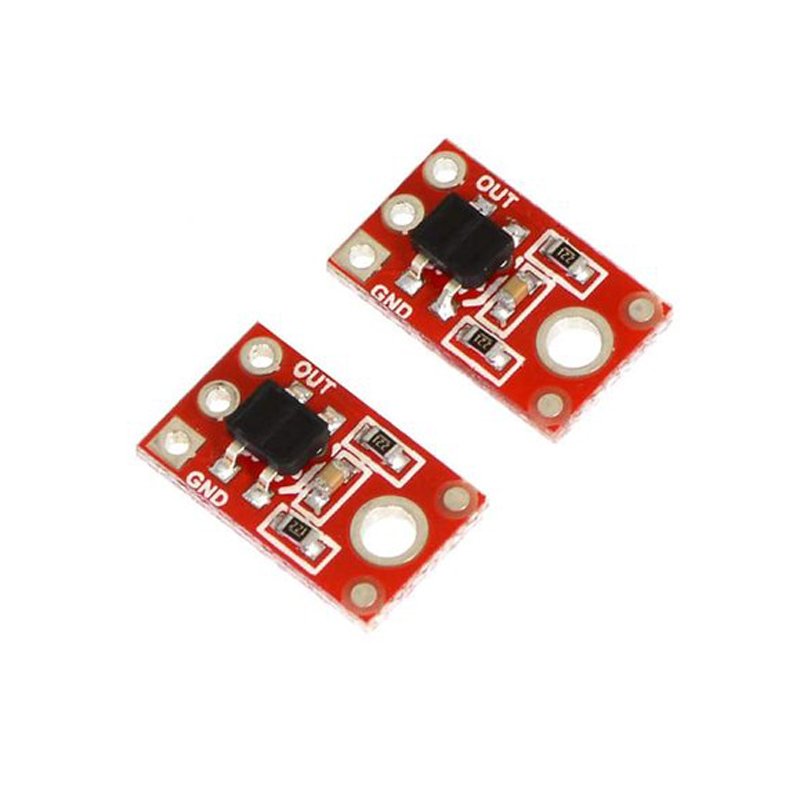
The QTR-1RC reflectance sensor carries a single infrared (IR) LED and phototransistor pair. To use the sensor, you must first charge the output node by applying a voltage to the OUT pin. You can then read the reflectance by withdrawing that externally applied voltage on the OUT pin and timing how long it takes the output voltage to decay due to the integrated phototransistor. Shorter decay time is an indication of greater reflection. This measurement approach has several advantages, especially when multiple units are used:
- No analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is required
- Improved sensitivity over voltage-divider analog output
- Parallel reading of multiple sensors is possible with most microcontrollers
The LED current-limiting resistor is set to deliver approximately 17 mA to the LED when VIN is 5 V. The current requirement can be met by some microcontroller I/O lines, allowing the sensor to be powered up and down through an I/O line to conserve power.
This sensor was designed to be used with the board parallel to the surface being sensed. Because of its small size, multiple units can easily be arranged to fit various applications such as line sensing and proximity/edge detection.
Specifications
- Dimensions: 0.3″ x 0.5″ x 0.1″ (without optional header pins installed)
- Operating voltage: 5.0 V
- Supply current: 17 mA
- Output format: digital I/O-compatible signal that can be read as a timed high pulse
- Optimal sensing distance: 0.125″ (3 mm)
- Maximum recommended sensing distance: 0.375″ (9.5 mm)
- Weight without header pins: 0.008 oz (0.2 g)